Heating and Air Conditioning in Passive Wood Homes
In passive wooden houses, the need to heat and condition rooms can be met with minimal energy input. However, for this to be done effectively, it is essential to implement a smart strategy to optimize energy consumption while avoiding waste.
Watertight Houses
Passive wooden houses are designed for optimal air tightness, eliminating unwanted drafts. Clearly, a house with air seepage is difficult to heat and functions as an energy sieve. For this reason, the homes we build today are completely anchored in energy-efficient and airtight principles.
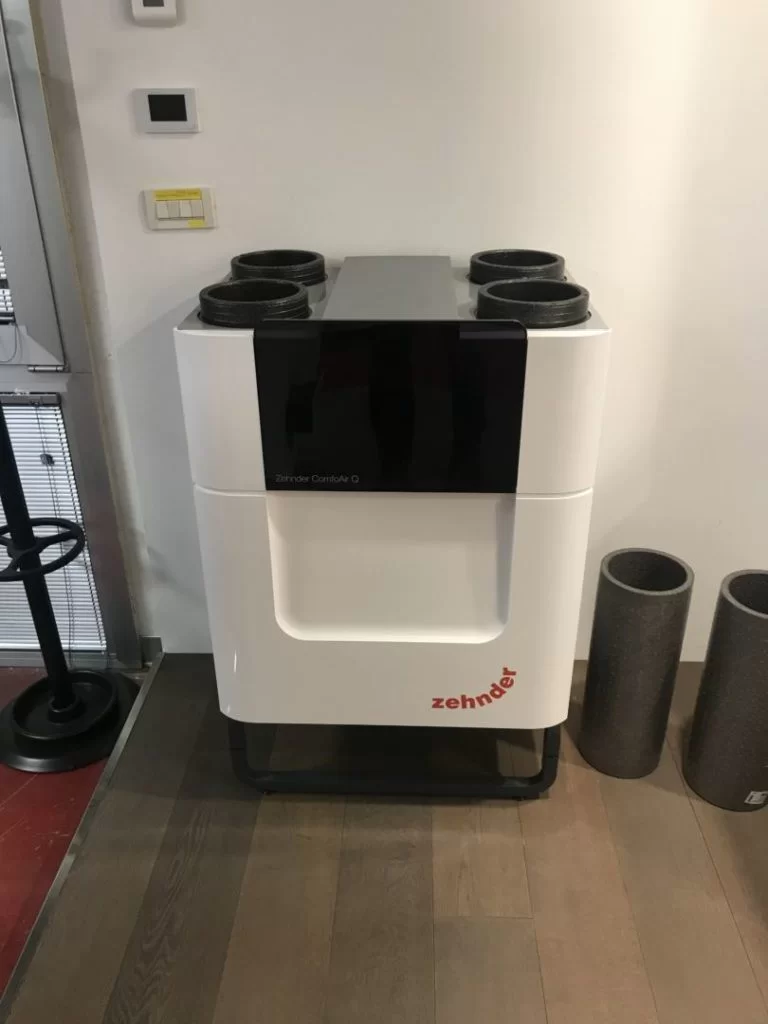

Importance of Air Exchange
In traditional buildings, drafts played a crucial role in ensuring air exchange. Previously, it was common to open windows to ventilate, but today, with the use of comforters and sheets always stretched taut, these practices are less common. Air exchange is just as important as heating itself, as it ensures a healthy microclimate inside the home. In summer, instead of putting in heat energy, it will be necessary to remove it, and this is the task of air conditioning. It is also essential to provide air dehumidification, greatly improving summer comfort. Central mechanical ventilation (CMV) is the ideal solution for achieving clean, fresh air. Among the European leaders in mechanical ventilation with heat recovery is Zehnder, a reliable Swiss company. You can find detailed information about their products by visiting their website: Zehnder Group Italia S.r.l..
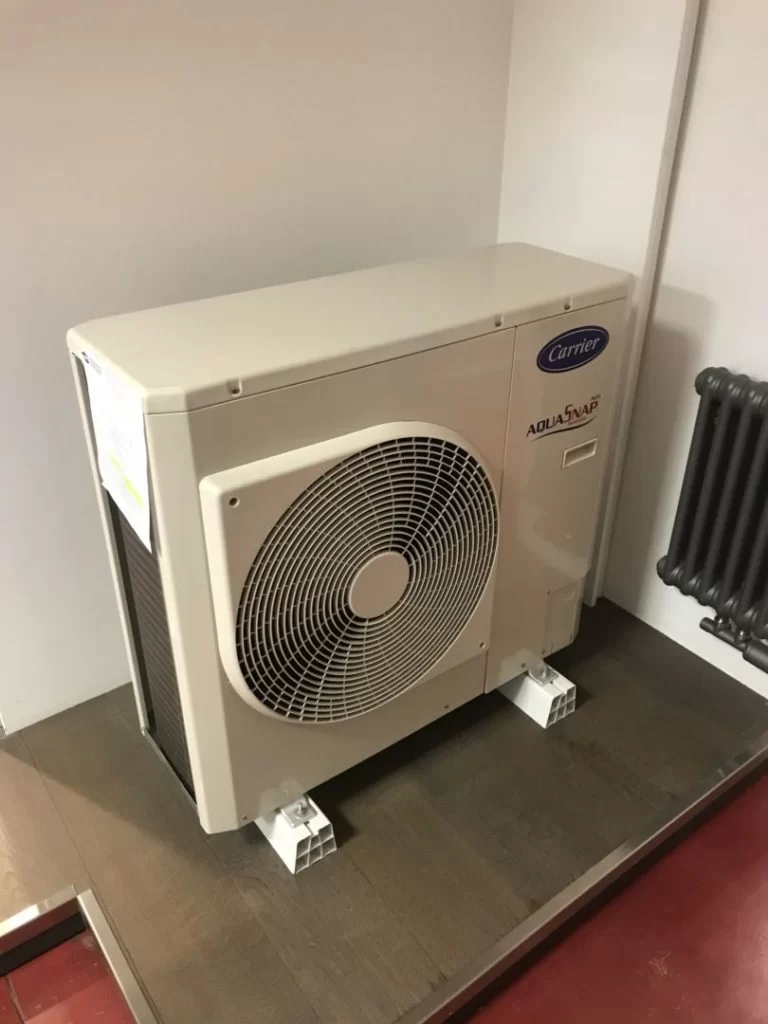

Heating and Cooling Methods
Today, heating and air conditioning are frequently done by heat pumps. Even gas boilers, in their most advanced version with heat recovery, remain polluting because they emit CO2. Heat pumps, in contrast, offer a double advantage: they heat in winter and cool in summer. There are two main systems for managing heating and cooling:
- Hydronic System
- Aeraulic System
In wooden houses, both systems can be used, depending on the preferences and needs of the users.
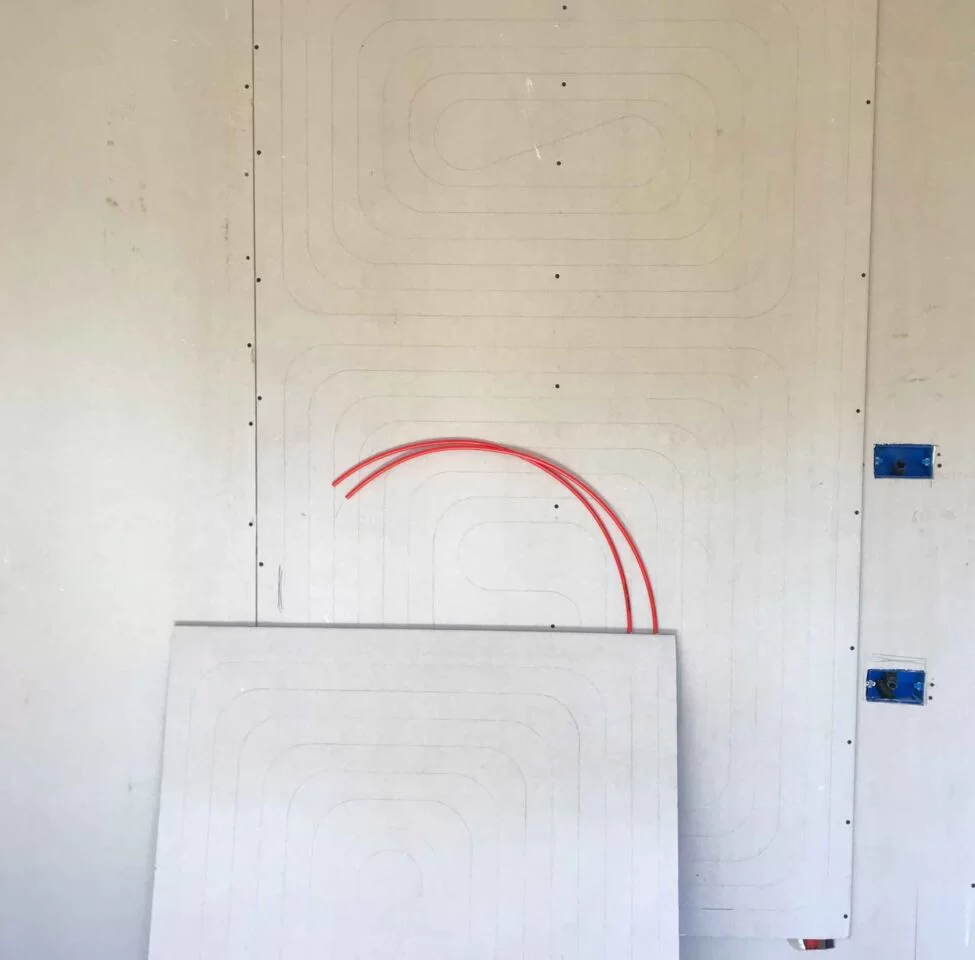

Hydronic System
The hydronic system uses a heat pump to heat or cool using water. The heat transferred to the water is then distributed to the room through radiant panels containing water-filled pipes.
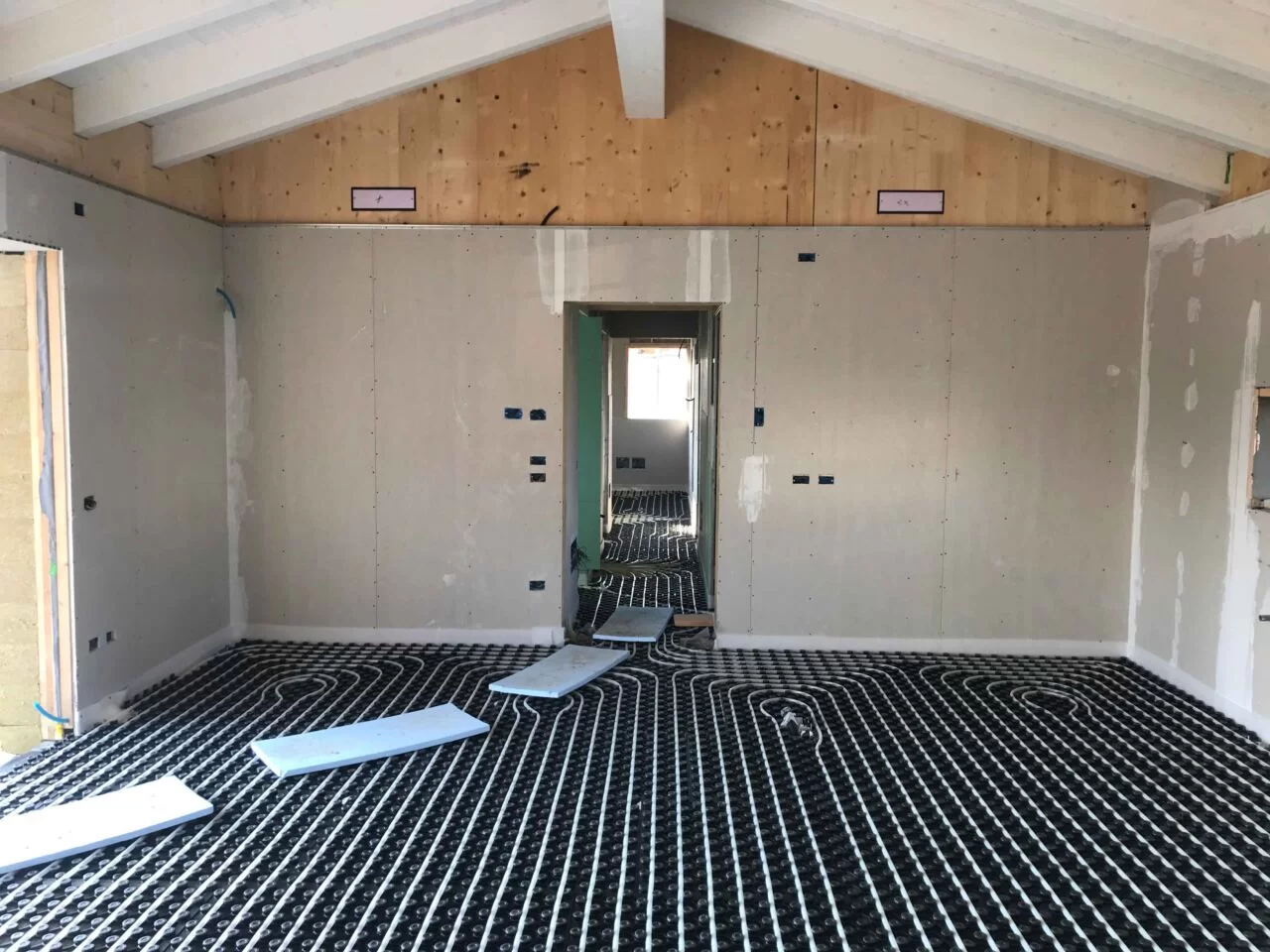

This system is traditional and well-established: radiant floors, for example, have been in use for more than 30 years. The hydronic heat pump heats water to a temperature of about 30 degrees, storing it in an inertial tank and flowing it into panels placed on the floor, wall or ceiling.
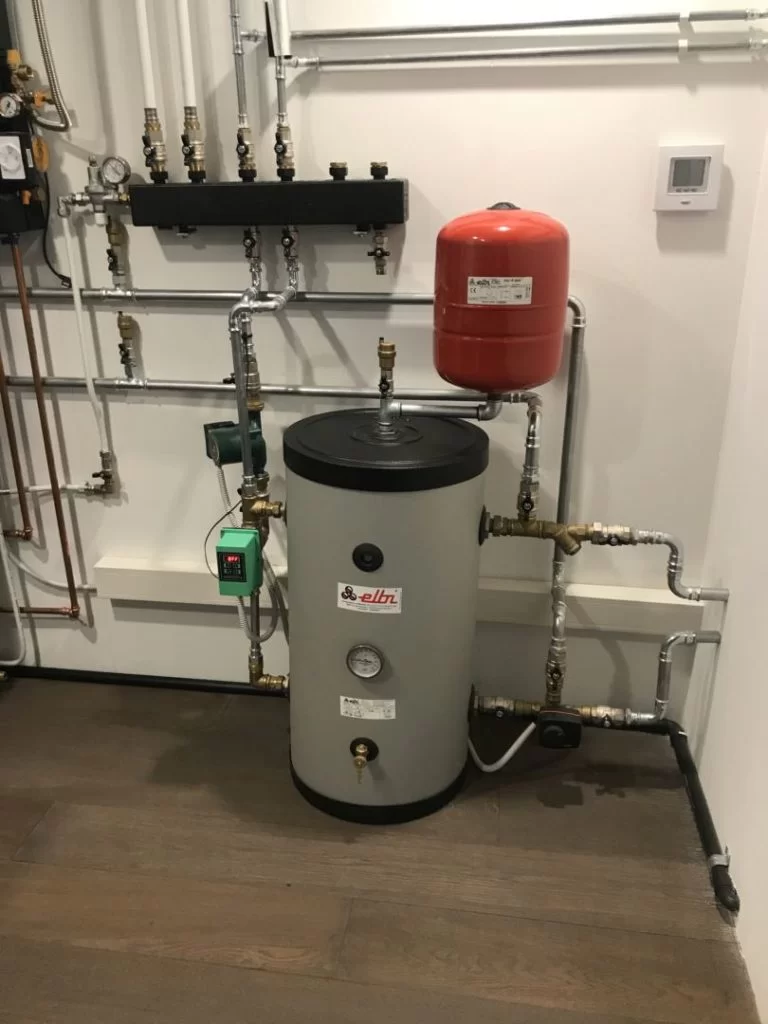

The main advantage of this system is that it produces radiant heat, providing optimal comfort without overheating the air by directly heating the body with a radiant effect. In addition, the same heat pump that heats water for space heating can also be used to heat domestic water.
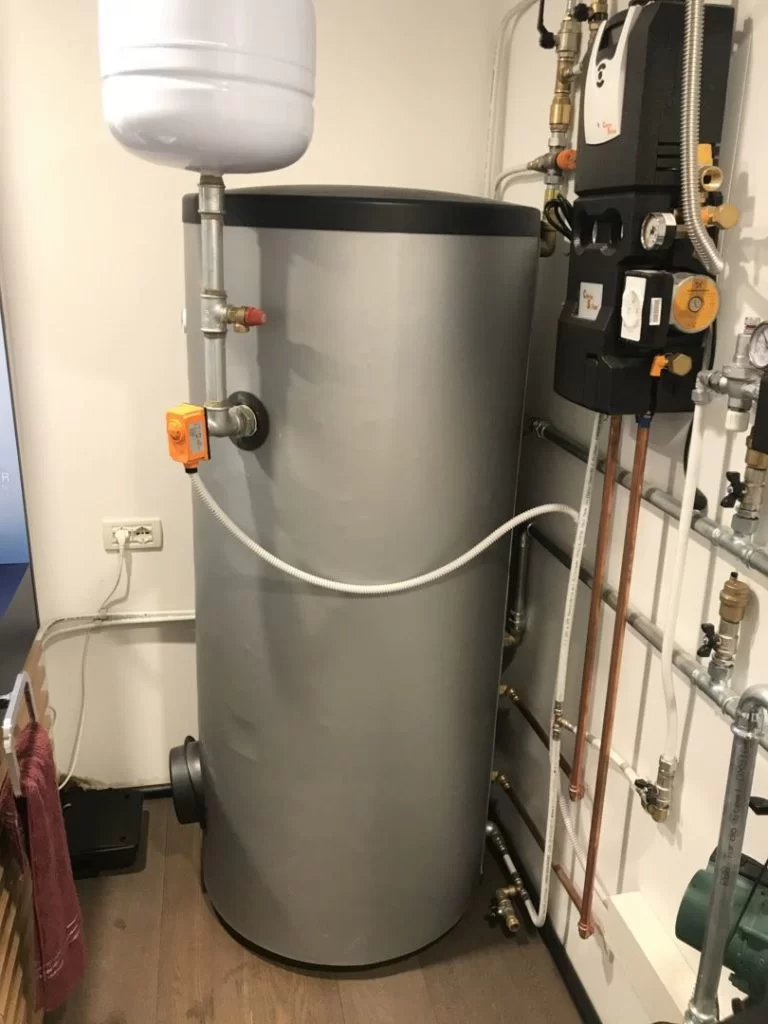

The hydronic system plans to work in conjunction with a VMC system especially in the summer period in which the VMC will need to provide air dehumidification.
Aeraulic System
The aeraulic system is designed to transfer heat to the environment by heating or cooling the air. These systems are equipped with mechanical ventilation and provide a significant supply of treated air, helping to maintain a comfortable and healthy indoor climate.
Characteristics of Aeraulic Systems
Aeraulic systems are composed of several components, including:
- Fans: Used to distribute treated air throughout the room.
- Heat exchangers: They enable the transfer of heat from outdoor air to indoor air, either in heating or cooling.
- Filters: They purify the air, removing dust and allergens, and ensuring a healthy environment for occupants.
Advantages of Aeraulic Systems in Wooden Houses.
- Climatic Comfort: With the ability to heat and cool quickly, these systems ensure comfortable temperatures in all seasons.
- Air Quality: By integrating filtration systems, aeraulic systems improve indoor air quality, reducing the presence of pollutants.
- Energy Efficiency: By using heat pumps in combination with mechanical ventilation, these systems can operate very efficiently, reducing energy costs.
- Installation Flexibility: Aeraulic systems can be adapted to different home configurations and integrated with other underfloor or radiant heating systems, ensuring tailor-made solutions for every need.
The Diffusion of Aeraulic Systems in Wooden Houses.
In recent years, aeraulic systems have been gaining popularity in passive wooden houses due to their ability to optimize comfort and energy efficiency. The combination of lightweight and highly insulating materials in wooden houses is a perfect match for the installation of these innovative solutions, which can help create an optimal microclimate and reduce overall energy demand. Implementing an aeraulic system inside wooden homes not only improves living comfort, but is also a sustainable choice, in line with modern trends of environmentally friendly and low-impact construction. Growing awareness about indoor air quality and energy conservation makes these systems increasingly popular among builders and homeowners.
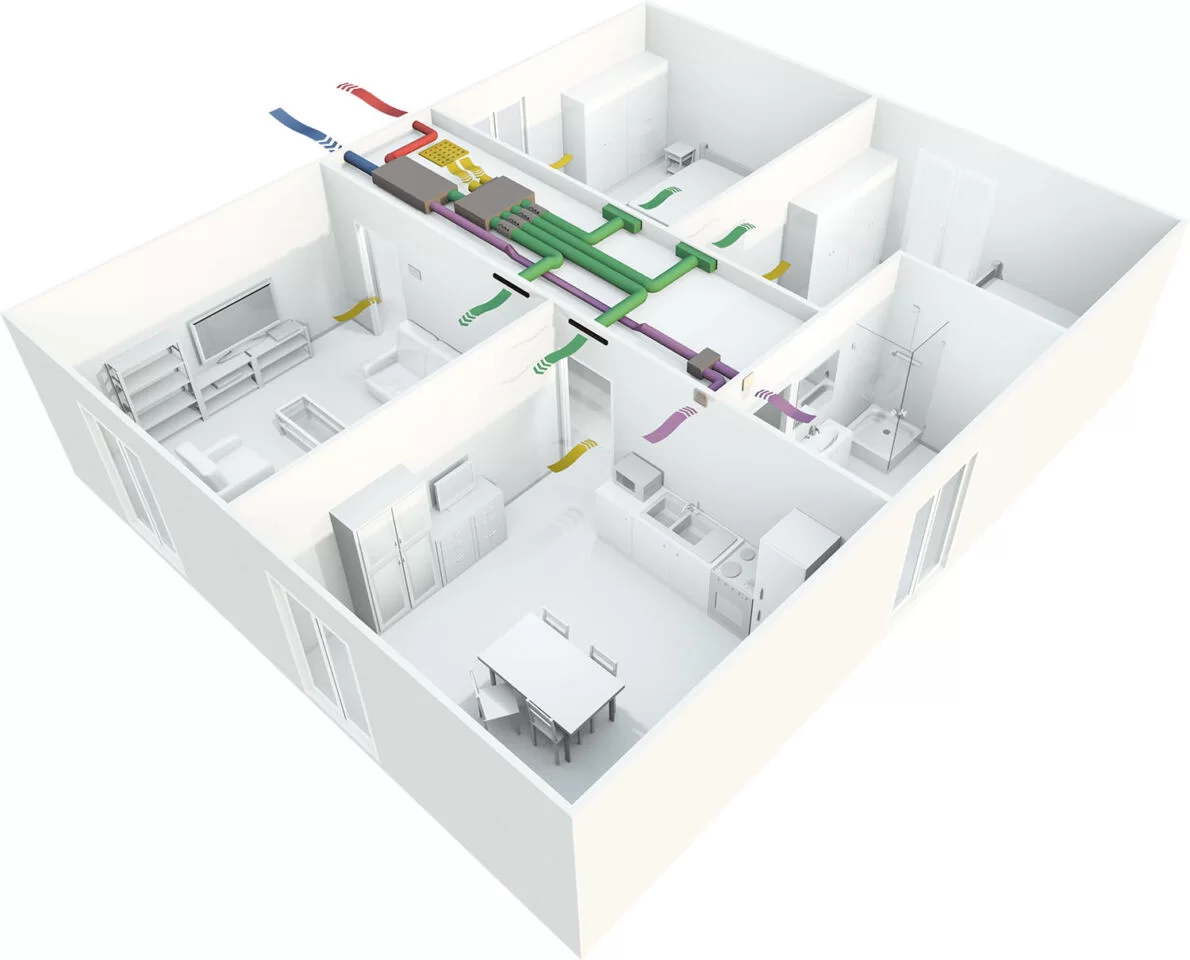
Perhaps the reason for the success of these systems is their ease of use. A single system with a single control system makes it very easy to program and manage the temperature even remotely.
Some firms such as Mylar https://it.mydatec.com/ call it Thermodynamic Mechanical Ventilation, others such as Irsap call it Adaptive Climate Ventilation https://www.irsap.com/it/ventilazione-meccanica-controllata/climatizzazione however, it is always a ventilation system enhanced by a heat pump. Nle case of Irsap the heat pump is external to the package and can be replaced or integrated freely.
Other alternatives
In the context of aeraulic systems, it is important to mention compact aggregate systems, which are an innovative solution for heating, air conditioning, ventilation and domestic hot water generation, all in a single unit. These compact systems, such as those produced by the Treviso-based company Brofer, optimize the use of space and increase the energy efficiency of homes.
Characteristics of Compact Aggregate Plants
- Multifunctional Integration: These systems combine several functions in one unit, simplifying installation and reducing space requirements. With this feature, there is no need to install several separate devices, making the system more compact and uncluttered.
- Suitable for Passive Houses: Compact aggregate systems are designed specifically for passive houses, where thermal insulation is of the highest standard. Their output is calibrated for rooms with low heat loss, ensuring optimal performance without wasting energy.
- Energy Efficiency: These devices can maximize energy efficiency through intelligent use of available resources, helping to reduce operating costs and minimize environmental impact.
- Easy Maintenance: Centralization of ventilation, heating, and air conditioning functions also facilitates maintenance operations, making these systems practical and convenient for owners.
A Sustainable Option
Opting for a compact aggregate system is not only a practical choice, but also a sustainable one. These systems reduce the ecological footprint of homes, contributing to a greener future and improved quality of life for occupants.
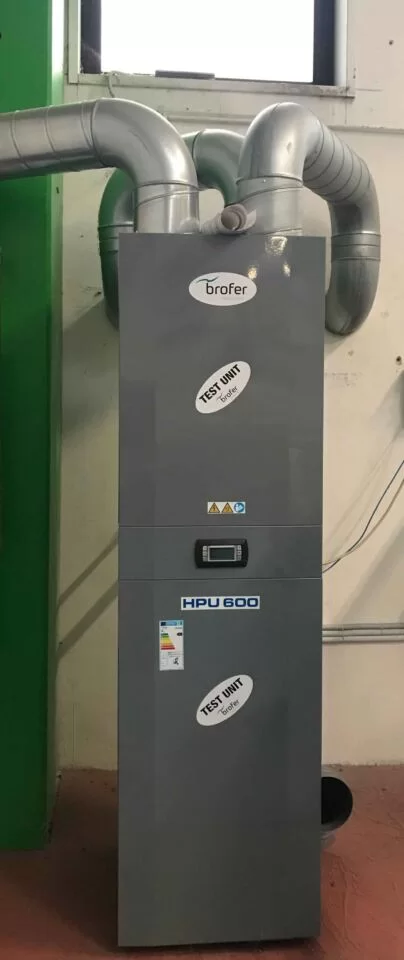

The size is that of a household refrigerator but in a small space it condenses the functions of a true central heating unit.
Conclusion
Heating and cooling systems, whether hydronic or aeraulic, are critical to ensuring a high standard of comfort in passive wooden houses. Choosing the right system for your needs is a crucial step in optimizing energy efficiency and improving the quality of life inside your home. Investing in innovative and sustainable technologies is the future choice for those who want to live in a healthy and comfortable environment.
